- Wheatstone Bridge
- Principle of Wheatstone Bridge
- Balanced Wheatstone Bridge
- Unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge
- Applications of Wheatstone Bridge
- Kelvin's Double Bridge
It is an arrangement of four resistances devised by Charles Wheatstone which is used to measure an unknown resistance.
Principle of Wheatstone Bridge
The Wheatstone bridge principle states that if four resistances P, Q, R, and S are arranged to form a bridge with a cell and key between A and C, and a galvanometer between B and D then the bridge is said to be balanced when the galvanometer shows a zero deflection.In balanced condition$\mathrm{I}_{9}=0 \quad$ so $\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{B}}=\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{D}}$ or $\frac{P}{Q}=\frac{R}{s}$. This is called condition of balance.
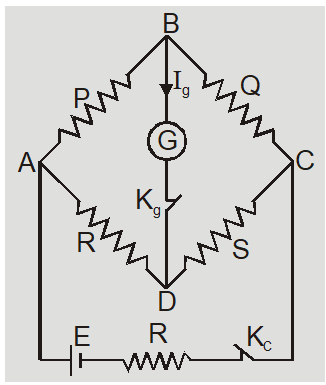
Balanced Wheatstone Bridge
The condition of balance depends on resistance P, Q, R, and S. This is independent of the emf of the battery.In-state of balance, the cell and galvanometer can be interchanged. While performing an experiment at start press the cell key $K_{c}$ first and then the galvanometer key $\mathrm{K}_{9}$ and at end remove $\mathrm{K}_{9}$ first and then $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}$ to avoid induced effects.
P and Q are called ratio arms, R is the known resistance arm and S is the unknown arm. BD and AC are called conjugate arms.
The resistance of a balanced Wheatstone bridge between A and C is $\frac{(P+Q)(R+S)}{P+Q+R+S}$.
The sensitivity of the bridge depends upon the value of resistances. The sensitivity is maximum when P, Q, R, and S are of the same order.
Unbalanced Wheatstone bridge
If $\frac{P}{Q}<\frac{R}{s}$ then $V_{B}>V_{D}$ so current flows from $B$ to $D .$
If $\frac{P}{Q}>\frac{R}{s}$ then $V_{B}
Browse More Topics Related to Wheatstone Bridge
Applications of Wheatstone Bridge
The Wheatstone Bridge has many uses in electronic circuits other than comparing an unknown resistance with a known resistance. When used with Operational Amplifiers, the Wheatstone bridge circuit can be used to measure and amplify small changes in resistance, RX due.Wheatstone bridge is not suitable for measurement of very small and very high resistances. Very low resistances are measured by Kelvin’s double bridge while very high resistances by leakage method.
For Complete Study Material and Video Tutorials for JEE & NEET Exam Preparation Download eSaral APP Also Read:
- Types and Effects of Electric Current
- Ohm’s Law and Resistance
- Combination of Resistances
- EMF and Internal Resistances of a Cell
- Cells Connected in Series, parallel and Mixed
- Kirchhoff’s Circuit Law
- Electric Currents in Conductors
- Wheatstone Bridge
- Post office Box
- Wheatstone Meter Bridge
- Moving Coil galvanometer
- Ammeter and Voltmeter
- Potentiometer Working Principle
